The concept and classification of GuillainBarre syndrome and related disorders // Cochrane Database syst Rev Pediatric GuillainBarré syndrome Prof Dr Saad S Al Ani 6 Kuwabara S GuillainBarré syndrome epidemiology, pathophysiology and Pathophysiology Two pathophysiological forms have been described Demyelinating form of GBS– GBS is a serious neurological disorder that results from the inflammation of peripheral nerves after certain events such as an infection 2 What are the symptoms of GBS?GUILLAINBARRE SYNDROME PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Predisposing Factors Precipitating Factors Age Post infection to Campylobacter jejuni Sex Poor hygiene Stress Diet Lifestyle Camlobacter e uni Enters the body by the use of multifenestrated cells or other mechanisms Innate immune response results in the uptake of the pathogens by immature antigen presenting cells

Risk Of Psychiatric Disorders In Guillain Barre Syndrome A Nationwide Population Based Cohort Study Journal Of The Neurological Sciences
Pathophysiology of guillain barre syndrome pdf
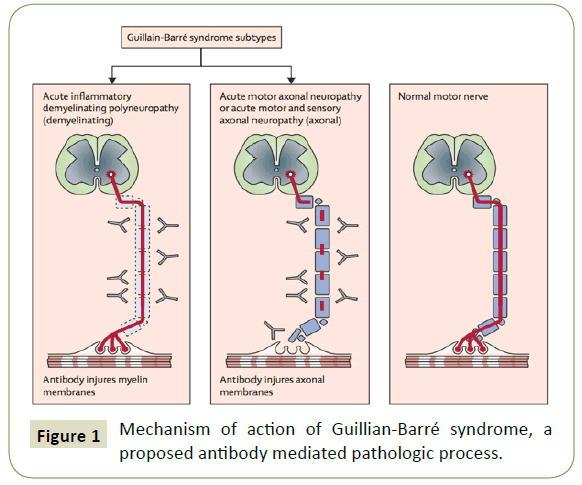
Pathophysiology of guillain barre syndrome pdf-GuillainBarré syndrome Pathogenesis The acute immunemediated polyneuropathies are classified under the eponym GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS), after the authors of early descriptions of the disease GBS is an acute monophasic paralyzing illness, usually provoked by GBS is one of the few leading causes of acute flaccid paralysis in developed countries and can present with varying degrees of weakness, sensory abnormalities, and autonomic dysfunction Even though the exact pathophysiology is still unknown, it is believed that an autoimmune response plays a role in the pathogenesis of this disease




Guillain Barre Syndrome In Denmark Validation Of Diagnostic Co Clep
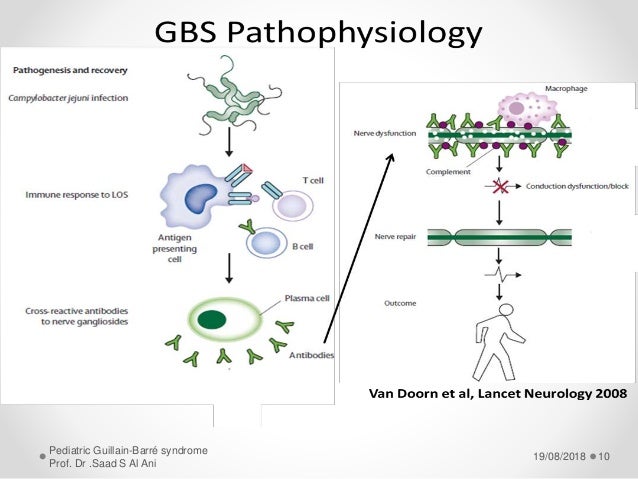
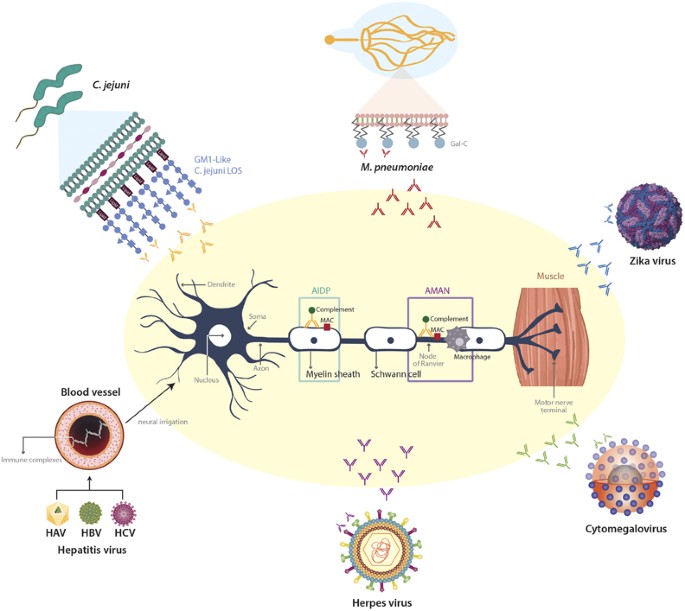
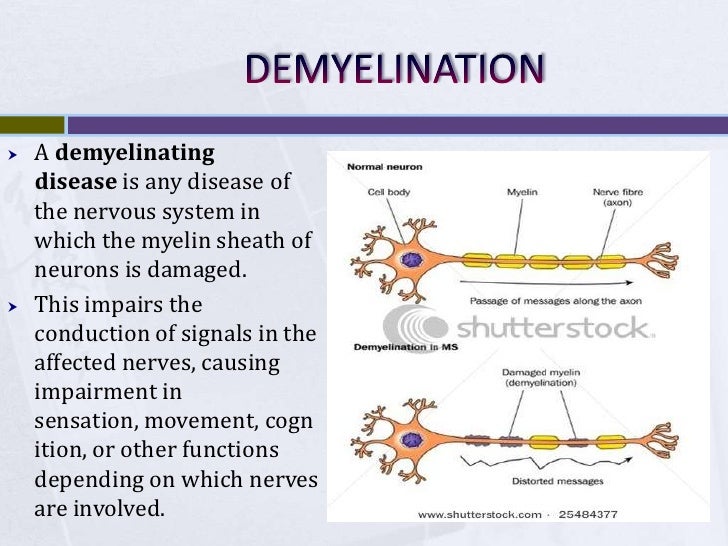
Guillain Barré syndrome is one of the best examples of a post infectious immune disease and offers insights into the mechanism of tissue damage in other more common autoimmune diseases Controlled epidemiological studies have linked it to infection with Campylobacter jejuni in addition to other viruses including cytomegalovirus and Epstein Barr virus In GuillainBarre syndrome, your immune system — which usually attacks only invading organisms — begins attacking the nerves In AIDP, the most common form of GuillainBarre syndrome in the US, the nerves' protective covering (myelin sheath) is damaged The damage prevents nerves from transmitting signals to your brain, causing weakness, numbness orFisher's syndrome, and postulated that this set of features was a form of GuillainBarré syndrome13 Patients with Fisher's syndrome may have facial and lower cranialnerve involvement Overlap forms of Fisher's syndrome with limb weakness and respiratory involvement are not uncommon Formes frustes are sometimes encountered
DOI /NEJMra The Guillain–Barré syndrome is the most frequent cause of Causes GuillainBarré syndrome is often preceded by an infection This could be a bacterial or viral infection GuillainBarré syndrome may also be triggered by vaccine administration or surgery In the context of Zika virus infection, unexpected increase in cases of GuillainBarré syndrome has been described in affected countriesGuillainBarre syndrome is an acute inflammatory polyneuropathy that is classified according to symptoms and divided into axonal and demyelinating forms Twothirds of patients have a history of gastroenteritis or influenzalike illness weeks before onset of neurologic symptoms
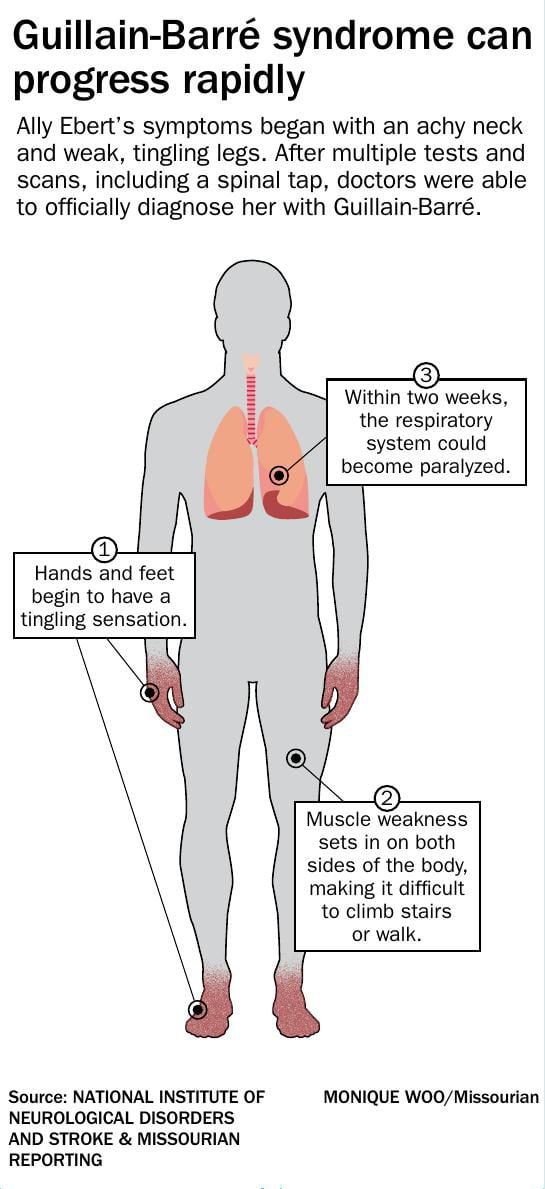
Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rapidonset muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system Typically, both sides of the body are involved, and the initial symptoms are changes in sensation or pain often in the back along with muscle weakness, beginning in the feet and hands, often spreading to the arms and upper bodyCitation Hernandez BA , Mendez FM, Elosegui IM (18) Recurrent Guillain Barre Syndrome J Neurol Neurosci Vol9 No4266 Abstract Introduction Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS) is an acute and mix demyelinating polyneuroradiculopathy of autoimmune cause It produces a flaccid autoimmune paralysisView Pathophysiology GuillainBarre Syndrome and Cauda Equina Syndromepdf from SCIENCE 101 at Kennett High School Possible Diagnosis (listed in order of likelihood) Signs and Symptoms seen in




Guillain Barre Syndrome The Lancet




Role Of Campylobacter Jejuni Infection In The Pathogenesis Of Guillain Barre Syndrome An Update
GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) is an important cause of acute neuromuscular paralysis Molecular mimicry and a crossreactive immune response play a crucial part in its pathogenesis, at least in those cases with a precedingM Ãirst described by Landry in 1859, occurs throughout the world, affects children adults of both sexes, but is more prevalent on men, and all age groups equally, and occurs in all seasons of the year m Commonly caused by viral agents À À ¦ ½ ½ m An increased incidence of GuillainBarré syndrome occurred after influenza vaccination in therefore, the syndrome continuesGuillainBarre Syndrome typically presents about two to four weeks after a patient has had a "relatively benign respiratory or gastrointestinal illness" (Andary, 14) Weakness in the lower extremities normally occurs and it may progress into the arms, trunk muscles, cranial nerves and the respiration muscles
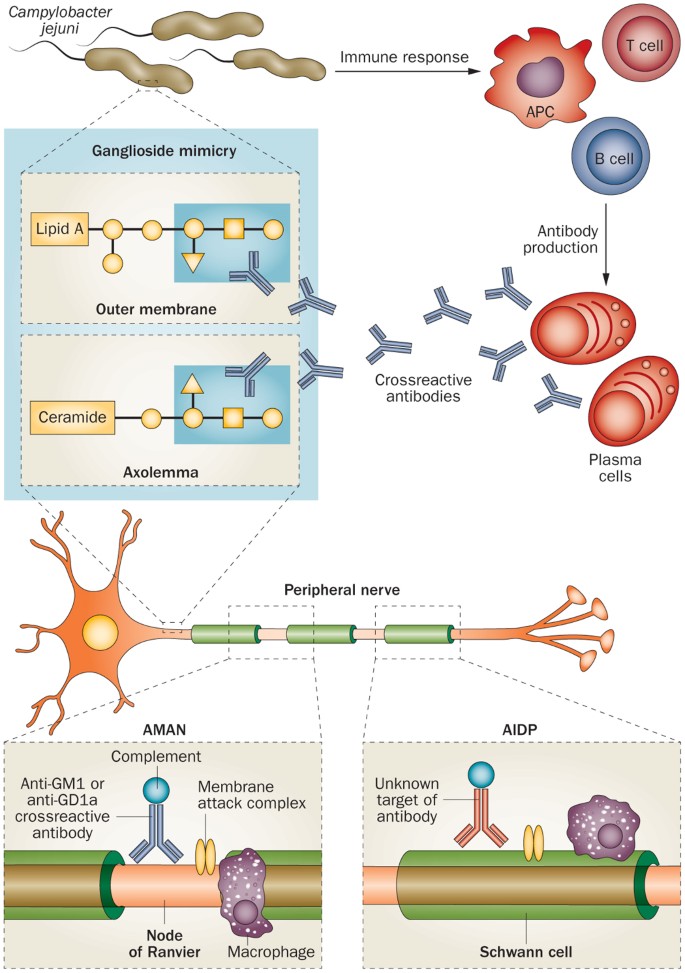



Guillain Barre Syndrome Pathogenesis Diagnosis Treatment And Prognosis Nature Reviews Neurology




Guillain Barre Syndrome Mayo Clinic Proceedings
GuillainBarre´ Syndrome Ted M Burns, MD1 ABSTRACT GuillainBarre´ syndrome (GBS) is an acuteonset, monophasic, immunemediated polyneuropathy that often follows an antecedent infection The diagnosis relies heavily on the clinical impression obtained from the history and examination, although cerebroGuillainBarré Syndrome (GBS), sought a means to help others deal with this disorder She brought some recovered patients together around her dining room table in suburban Philadelphia to start a support organization Attending this meeting were Joel Steinberg, a Guillain barre syndrome (gbs) 1 GuillainBarre Syndrome (GBS( Dr Mohamed Abunada Pediatric Neurology Department Dr Al rantisi specialized children Hospital 2 Outline Definition Epidemiology Etiology Pathogenesis & Pathology Clinical features Investigations Diagnosis Differential diagnosis Treatment Prognosis 3



Guillain Barre Syndrome



Guillain Barre Syndrome Clinical Profile Journal Of Current Medical Research And Opinion
What is GuillainBarre syndrome, and can you get it from the J&J vaccine?– Illness is typically characterized by Abstract Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS), a disease affecting the peripheral nervous system, is now well known However, the disease concept has evolved over successive periods For example, for approximately nine decades from the first report of GBS, it was considered to have a spinal cord origin After the first clinical report, the accumulation of detailed




Pdf Biomarkers Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Some Recent Progress More Still To Be Explored Semantic Scholar




Guillain Barre Syndrome Ppt Download
Classical GuillianBarré Syndrome (GBS) • As described by Landry in 2 1 Landry O Gazette Hebdomadiare de Médecine et de Chirurgie 1859;6472–74 et 1859;6486–GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) can be described as a collection of clinical syndromes that manifests as an acute inflammatory polyradiculoneuropathy with resultant weakness and diminished reflexes With poliomyelitis under control in developed countries, GBS is now the most important cause of acute flaccid paralysisGuillainBarré syndrome is a clinically diagnosed disorder, but nerve conduction studies (NCS) can help to support the diagnosis, to discriminate between axonal and demyelinating subtypes, and could relate to prognosis Nerve conduction abnormalities are most pronounced 2 weeks after start of weakness 58




Guillain Barre Syndrome The Lancet




Guillain Barre Syndrome The Lancet
N Engl J Med 12; GuillainBarré syndrome is one of several disorders involving weakness due to peripheral nerve damage caused by the person's immune system While GBS comes on rapidly over days to weeks, and the person usually recovers, other disorders develop slowly andGuillainBarré Syndrome Fact Sheet 1 What is GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS)?




Guillain Barre Syndrome Mayo Clinic Proceedings



Severe Guillain Barrandeacute Syndrome Following Shingrix Sup Andreg Sup Vaccine Administration Insight Medical Publishing
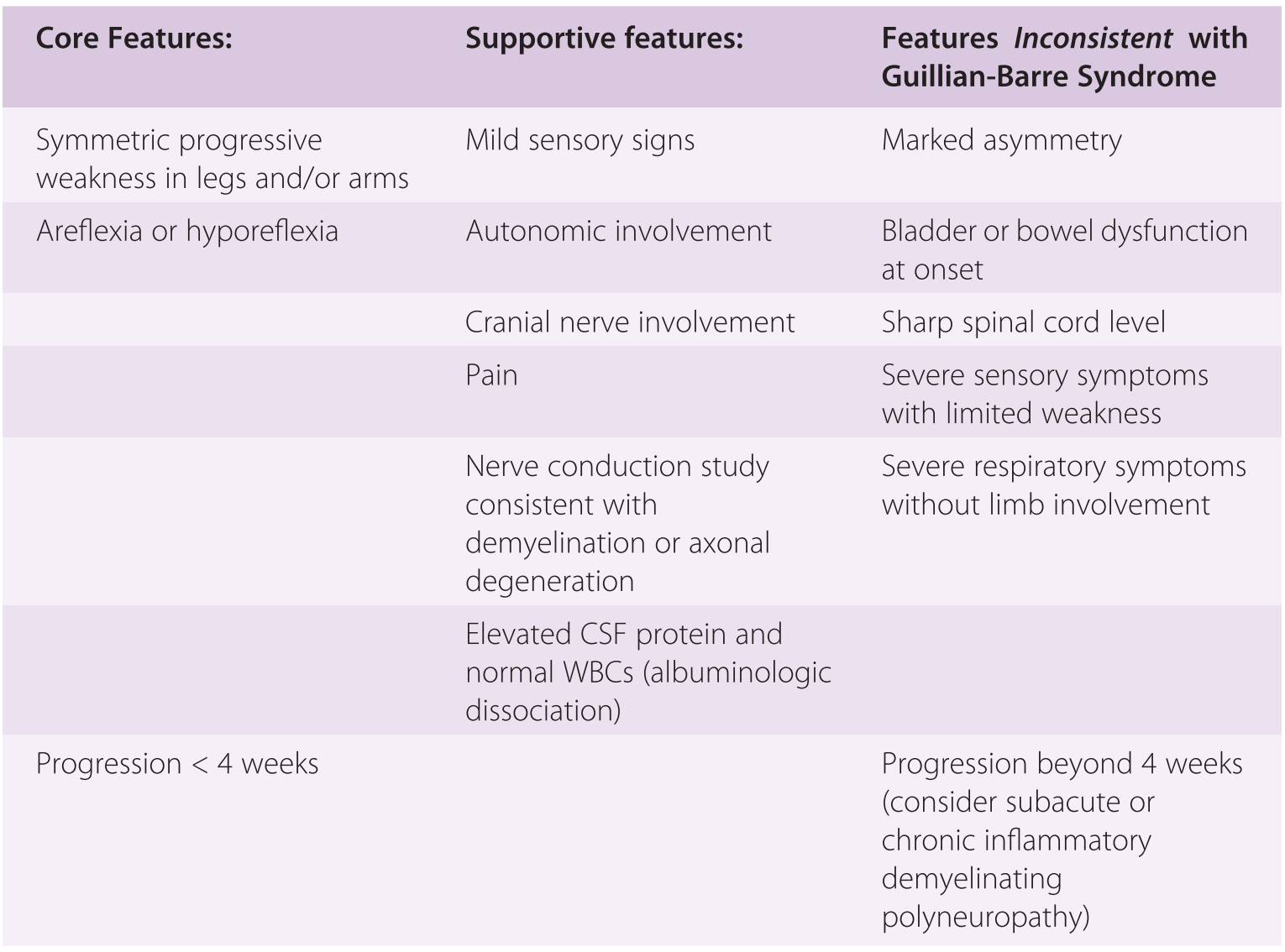
GuillainBarré Syndrome FS (E)indd 2 7/15/11 302 PM GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) can affect anybody It can strike at any age and both sexes are equally prone to the disorder The syndrome is rare, however, aflicting only about one person in 100,000 Usually GBS occurs a few days or weeks after the patient has had symptoms of a respiratoryAbstract GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) is clinically defined as an acute peripheral neuropathy causing limb weakness that progresses over a time period of days or, at the most, up to 4 weeks GBS occurs throughout the world with a median annual incidence of 13 cases per population of 100 000, with men being more frequently affected than women Etiology and Pathophysiology The mechanism of GBS is believed to be an inflammatory neuropathy due to cross reactivity between neural antigens and antibod GuillainBarre ´ Syndrome



2



1
GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) occurs when the immune system attacks the peripheral nervous system — the system of nerves that run though the body, outside the brain, and spinal cord It can cause muscle weakness, pain, changes in sensation (numbness or tingling), and sometimes even temporary paralysis of muscles in the legs, arms, face, andGuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) is a rare autoimmune disease in which your body's immune system damages your nerves It causes muscle weakness and sometimes paralysis Symptoms are mostly temporary and typically last anywhere from a few weeks to several yearsRopper, AH The GuillainBarre Syndrome – A free PowerPoint PPT presentation (displayed as a Flash slide show) on PowerShowcom id 45ba53MWZlY



Guillain Barre Syndrome And Myasthenia Gravis Chapter 43 Gupta And Gelb S Essentials Of Neuroanesthesia And Neurointensive Care




Efficacy Of Therapies In The Treatment Of Guillain Barre Syndrome A Network Meta Analysis Medrxiv
GuillainBarre syndrome is an acute inflammatory polyneuropathy that is classified according to symptoms and divided into axonal and demyelinating forms Twothirds of patients have a history of gastroenteritis or influenzalike illness weeks before onset of neurologic symptoms Associated with Zika virus outbreaksGuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) is an acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy In typical cases, the first symptoms of GBS are pain, numbness, paresthesia, weakness in the limbs Autonomic involvement is common and causes urinary retention andThe clinical spectrum of GuillainBarré syndrome is varied—at least three different types have been identified In Europe and North America about 95% of cases are acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathyandtheother5%areacuteaxonal motor disorder and acute sensory and motor




What S New In Guillain Barre Syndrome Postgraduate Medical Journal




Guillain Barre Syndrome Where Body S Immune System Attacks Its Nervous System Youtube
GuillainBarre syndrome (GBS) is the most common cause of acute, flaccid, neuromuscular paralysis in the United States GuillainBarre syndrome was first discovered more than a century ago Advances in the past century include investigating the immunemediated pathophysiology of the disease, recogniGuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) is a rare disorder in which a person's own immune system damages their nerve cells, causing muscle weakness and sometimes paralysis GBS can cause symptoms that usually last for a few weeks Most people recover fully from GBS, but some people have longterm nerve damage In very rare cases, people have died of Overview GuillainBarre syndrome (GBS) is an autoimmune and rapid (hour to weeks) but rare neurological disorder in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks part of its peripheral nervous system—the network of nerves present outside of the brain & spinal cord of the body GuillainBarre syndrome (GBS) can range from a very mild clinical case with a severe




Diagnosis And Treatment Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Journal Of Ethics American Medical Association



1
Continuing Education Activity GuillainBarre syndrome (GBS) is a rare but serious postinfectious immunemediated neuropathy It results from the autoimmune destruction of nerves in the peripheral nervous system causing symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and weakness that can progress to paralysisGuillainBarré syndrome is the most common cause of ascending neuromuscular flaccid paralysis in the developed world, 1,2 with annual incidence ofGuillain Barre Syndrome(gheeyanbar syndrome) also known as landry's palsy is a classic lower motor neuron disorder It is a reactive self limited autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system attacks part of the peripheral nervous system




Pdf Guillain Barre Syndrome Gbs A Review



2
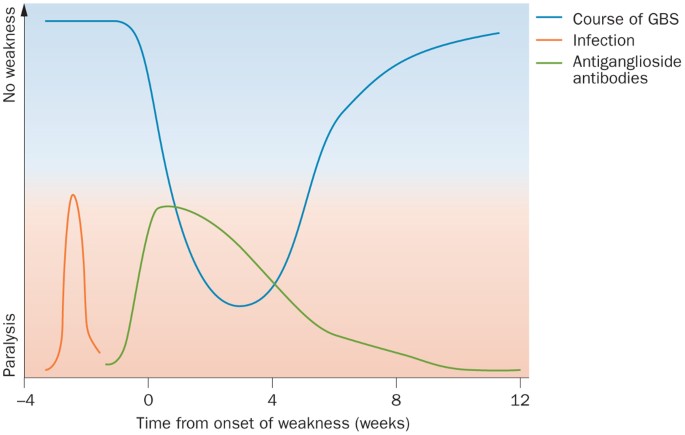
GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS), with an annual incidence of 1–2 per 100,000, is the most common cause of neuromuscular paralysis in the western world Even with modern intensive care and intravenous (iv) immunoglobulin (Ig) treatment there remains an associated mortality rate between 35% and 12% in the acute phase 1 and residual disabilityH GuillainBarre´ syndrome is the most frequent cause of acute or subacute flaccid weakness worldwide h Campylobacter jejuni is the most commonly identified organism associated with GuillainBarre´ syndrome h Approximately 50% of patients with GuillainBarre´ syndrome achieve maximum weakness by 2 weeks, 80% by 3 weeks, and 90% by 4 weeks h Thirty percent ofAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators



2




Final Gbs Pdf Clinical Medicine Medical Specialties
Plasmapheresis and acute GuillainBarre syndrome The GuillainBarre Syndrome Study Group Neurology 1984; GuillainBarré syndrome is the most common and most severe acute paralytic neuropathy, with about 100 000 people developing the disorder every year worldwide Pediatric GuillainBarré syndrome Prof Dr Saad S Al Ani 49 Peripheral neuropathies from the following may produce a GBSlike picture • Vincristine • Glue sniffing • Heavy metals poisoning • Organophosphate pesticides • HIV infection • Diphtheria • Lyme disease • Inborn errors of metabolism • Leigh disease • Tangier disease • Porphyria




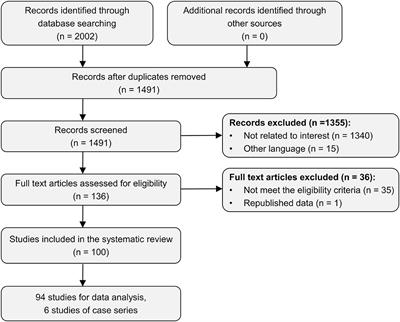
Flow Chart Of Recruitment Process Gbs Guillain Barre Syndrome Mh Download Scientific Diagram
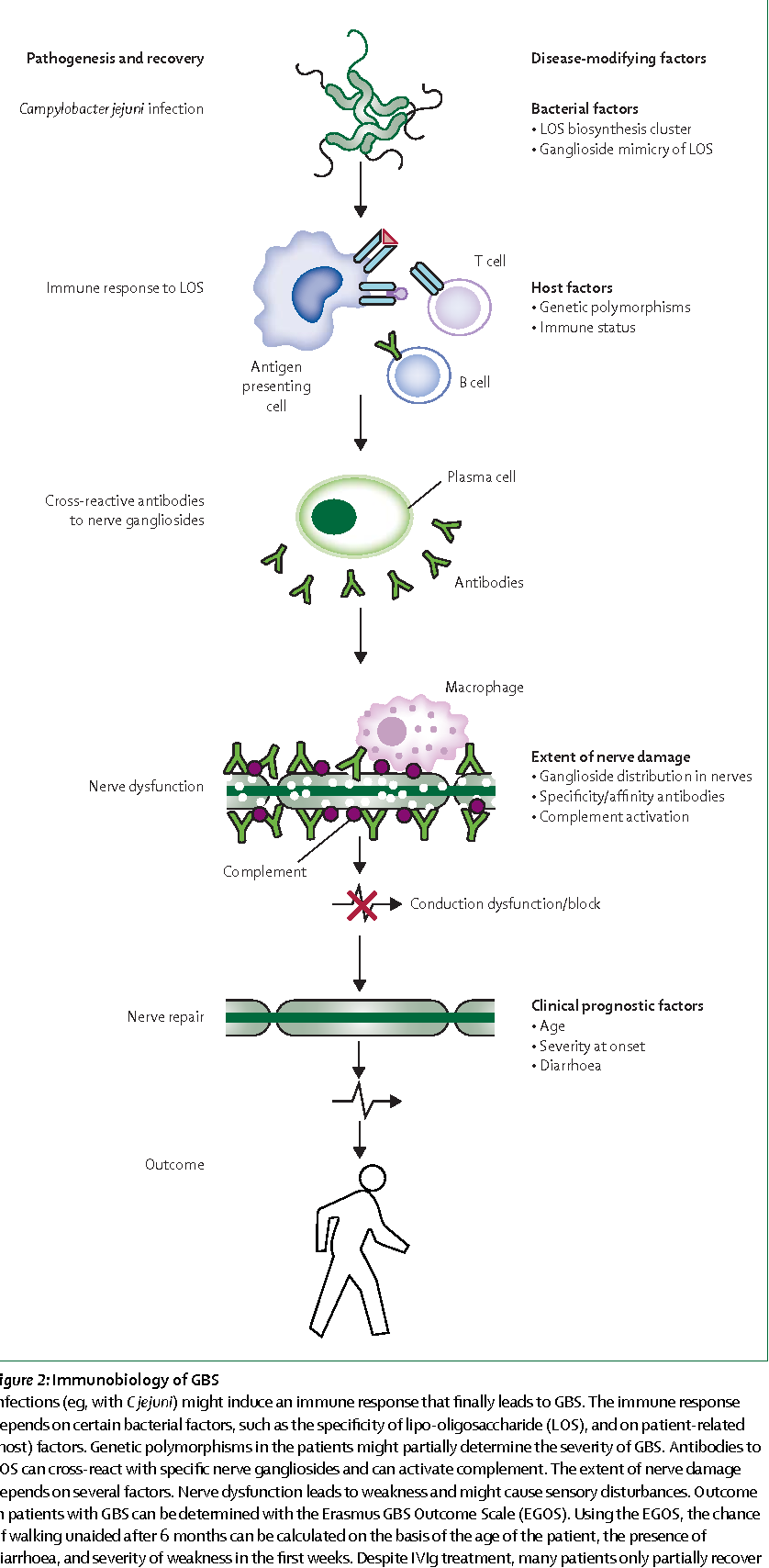



Pdf Clinical Features Pathogenesis And Treatment Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Semantic Scholar




Clinical Features Pathogenesis And Treatment Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Sciencedirect



Guillain Barre Syndrome Calgary Guide
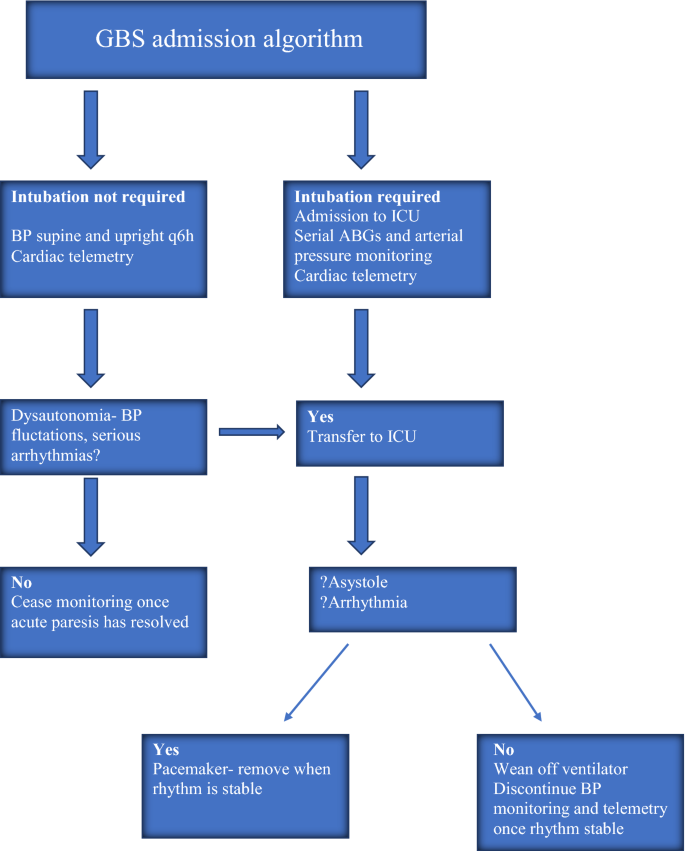



Autonomic Involvement In Guillain Barre Syndrome An Update Springerlink




Guillain Barre Syndrome The Lancet




Pdf Guillain Barre Syndrome Gbs An Orphan Disease




Guillain Barre Syndrome Gbs Emcrit Project




Guillain Barre Syndrome American Family Physician




Postoperative Guillain Barre Syndrome A Neurologic Complication That Must Not Be Overlooked A Literature Review Sciencedirect



Pathophysiology Of Guillain Barre Syndrome




Therapeutic Plasma Exchange In Guillain Barre Syndrome And Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy Sciencedirect



Atypical Guillain Barre In The Emergency Department The Western Journal Of Emergency Medicine



2



2



1



2




Guillain Barre Syndrome




Guillain Barre Syndrome The Lancet




Clinical Features Pathogenesis And Treatment Of Guillain Barre Syndrome The Lancet Neurology




Covid 19 And Guillain Barre Syndrome A Wellcome Open Research




Guillain Barre Syndrome In Denmark Validation Of Diagnostic Co Clep




Guillain Barre Syndrome And Myasthenia Gravis Chapter 43 Gupta And Gelb S Essentials Of Neuroanesthesia And Neurointensive Care
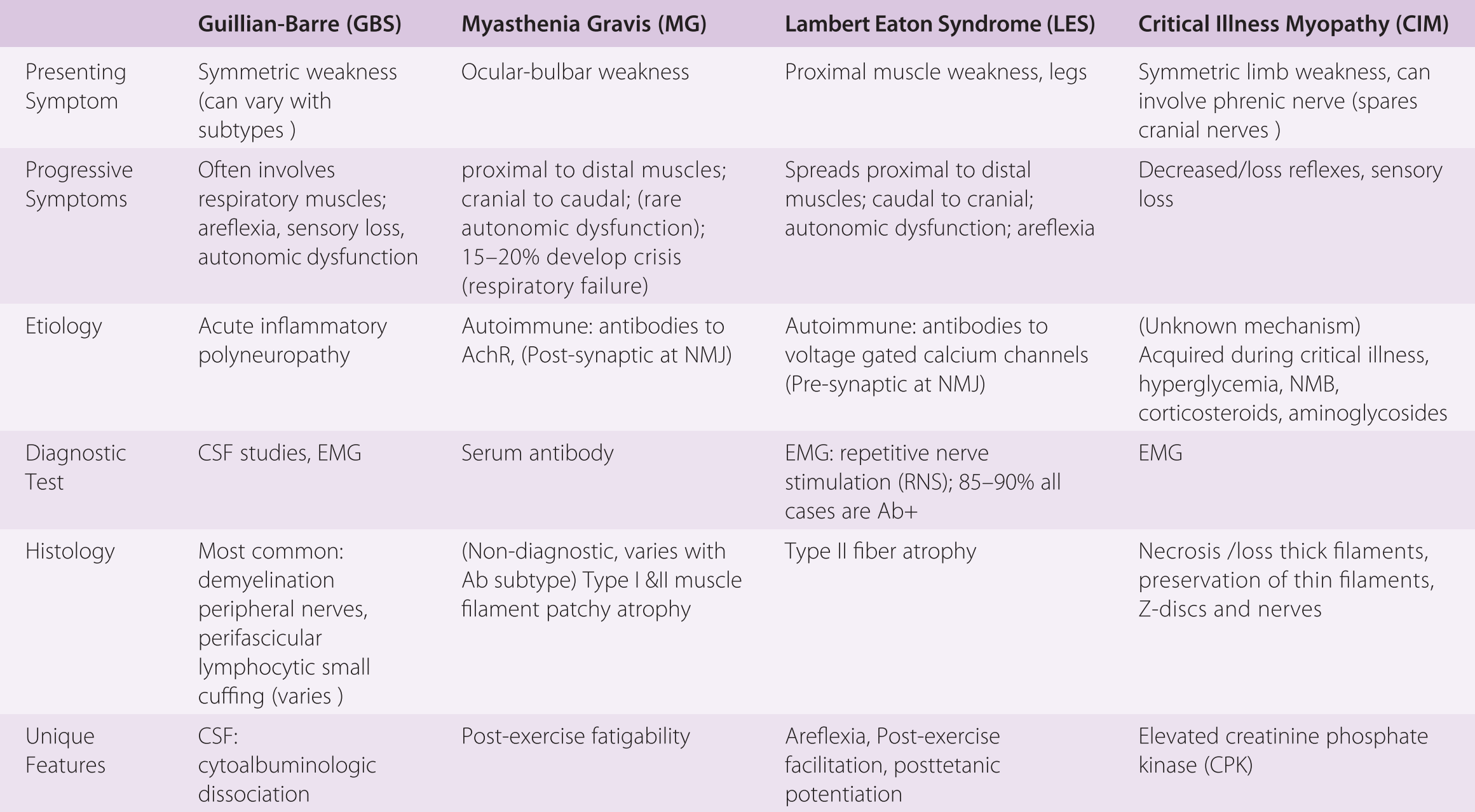



Guillain Barre Syndrome And Myasthenia Gravis Chapter 43 Gupta And Gelb S Essentials Of Neuroanesthesia And Neurointensive Care




Pdf Guillain Barre Syndrome And Matrix Metalloproteinases Semantic Scholar




Intravenous Immune Globulins In Patients With Guillain Barre Syndrome And Contraindications To Plasma Exchange 3 Days Versus 6 Days Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry




What S New In Guillain Barre Syndrome Practical Neurology




Original Research Second Ivig Course In Guillain Barre Syndrome With Poor Prognosis The Non Randomised Isid Study Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry




Altered Mental Status In Guillain Barre Syndrome A Noteworthy Clinical Clue Mulroy Annals Of Clinical And Translational Neurology Wiley Online Library




Guillain Barre Syndrome American Family Physician




Pdf The Development Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Gbs In Association Withconfirmed Lyme Disease A Potential Autoimmune Response In Gbs Secondaryto Tick Borne Diseases Semantic Scholar




Pathogenesis Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Gbs And Chronic Download Scientific Diagram




Pdf Guillain Barre Syndrome Prevalence And Long Term Factors Impacting Bladder Function In An Australian Community Cohort
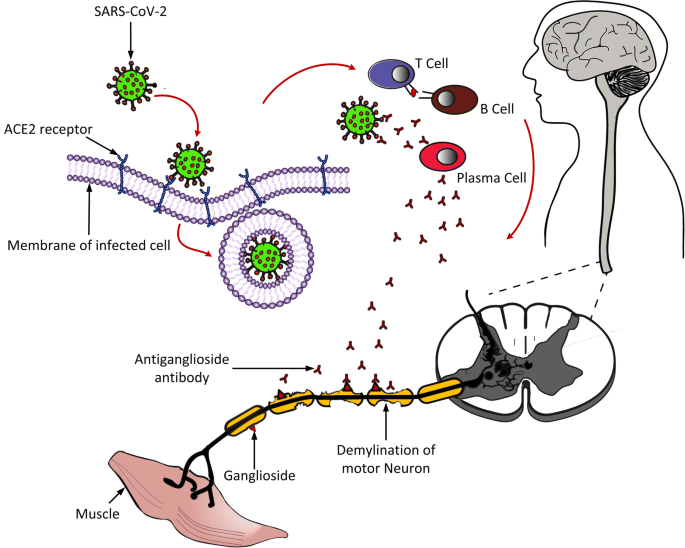



Covid 19 Associated Guillain Barre Syndrome Atypical Para Infectious Profile Symptom Overlap And Increased Risk Of Severe Neurological Complications Springerlink




Guillain Barre Syndrome Pdf Clinical Medicine Medical Specialties



Guillain Barre Syndrome Transverse Myelitis And Infectious Diseases Cellular Molecular Immunology



Guillain Barre Syndrome Pathogenesis Diagnosis Treatment And Prognosis Nature Reviews Neurology




Risk Of Psychiatric Disorders In Guillain Barre Syndrome A Nationwide Population Based Cohort Study Journal Of The Neurological Sciences



Guillain Barre Syndrome In 2 Patients With Covid 19 The Egyptian Journal Of Neurology Psychiatry And Neurosurgery Full Text



Frontiers Trauma Related Guillain Barre Syndrome Systematic Review Of An Emerging Concept Neurology




What S New In Guillain Barre Syndrome Postgraduate Medical Journal



2
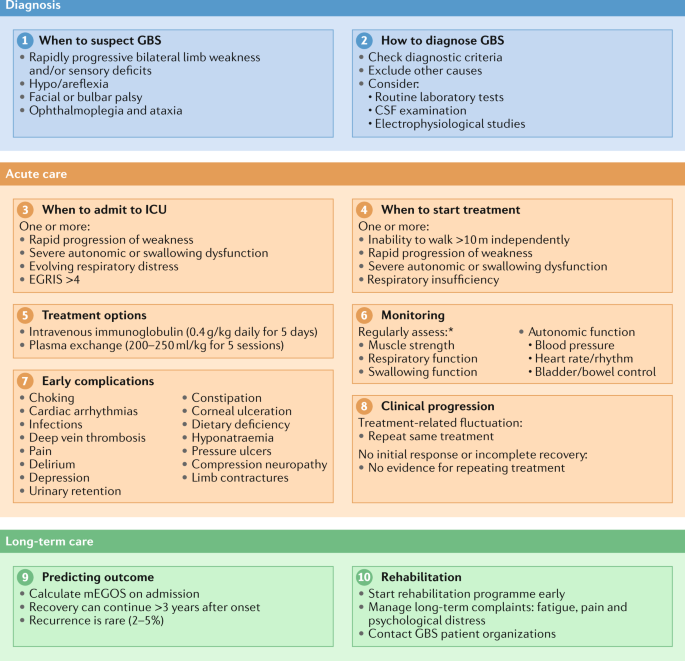



Diagnosis And Management Of Guillain Barre Syndrome In Ten Steps Nature Reviews Neurology
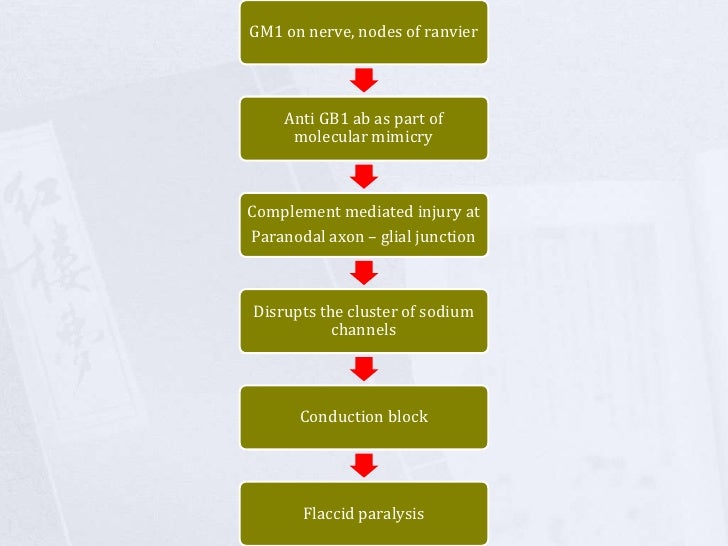



Guillain Barre Syndrome
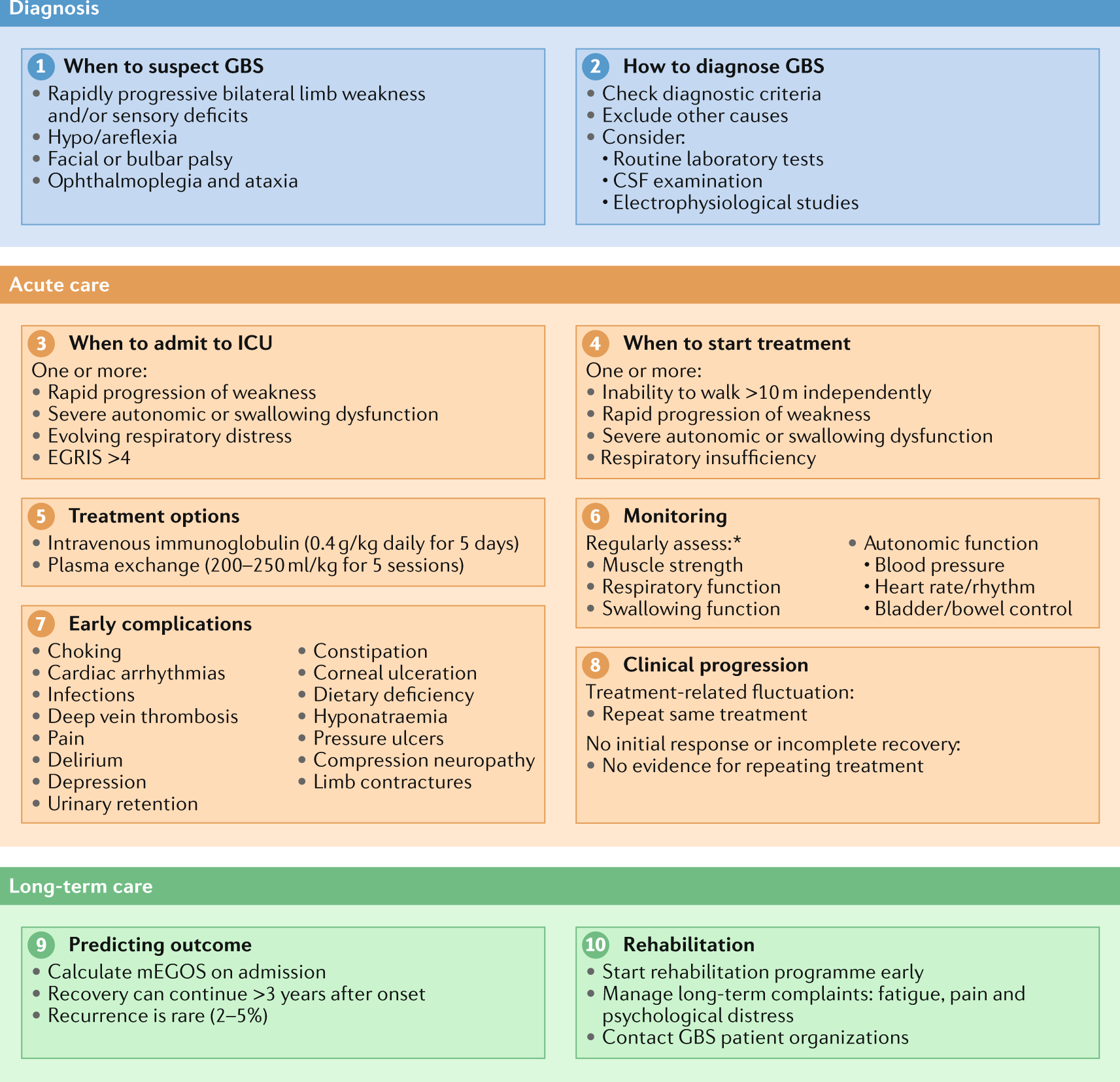



Diagnosis And Management Of Guillain Barre Syndrome In Ten Steps Nature Reviews Neurology
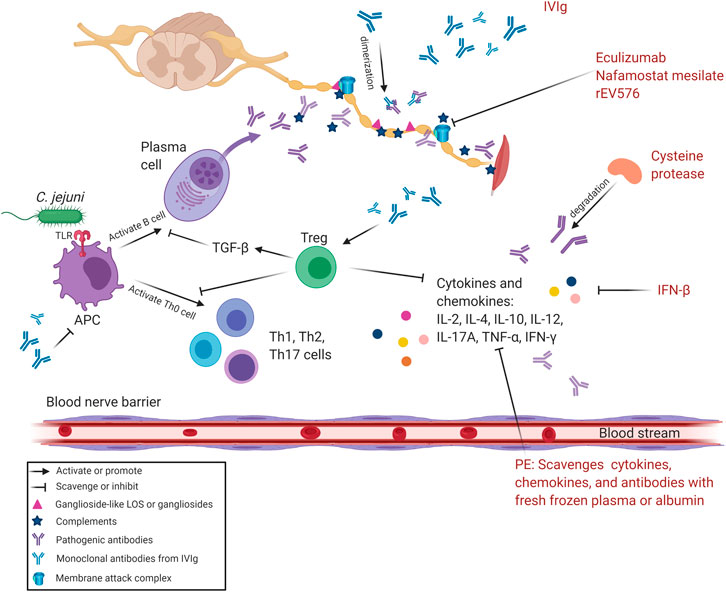



Frontiers Intensive Care And Treatment Of Severe Guillain Barre Syndrome Pharmacology




Clinical Variants Of Guillain Barre Syndrome In Children Pediatric Neurology




Incidence Clinical Risk Factors And Outcomes Of Guillain Barre In Covid 19 Fragiel 21 Annals Of Neurology Wiley Online Library



Guillain Barre Syndrome



Guillain Barre Syndrome What Is It And Why Should You Care News Columbiamissourian Com




The Management Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Current Paediatrics




Guillain Barre Syndrome American Family Physician




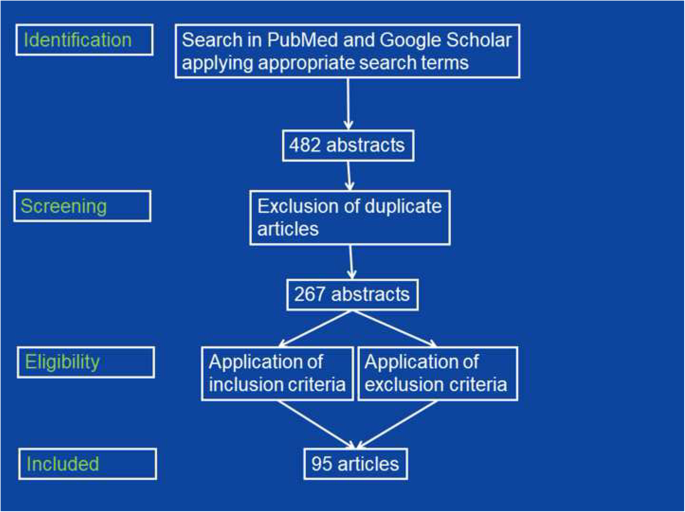
Flow Chart Used To Select Articles Related To Etiology Of Download Scientific Diagram
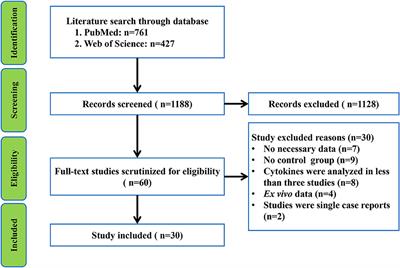



Frontiers Peripheral Blood And Cerebrospinal Fluid Cytokine Levels In Guillain Barre Syndrome A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Neuroscience




Prevalence And Outcomes Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Among Pediat Ndt




Role Of Campylobacter Jejuni Infection In The Pathogenesis Of Guillain Barre Syndrome An Update




Safety And Efficacy Of Eculizumab In Guillain Barre Syndrome A Multicentre Double Blind Randomised Phase 2 Trial The Lancet Neurology




Review Article On Covid 19 And Guillain Barre Syndrome
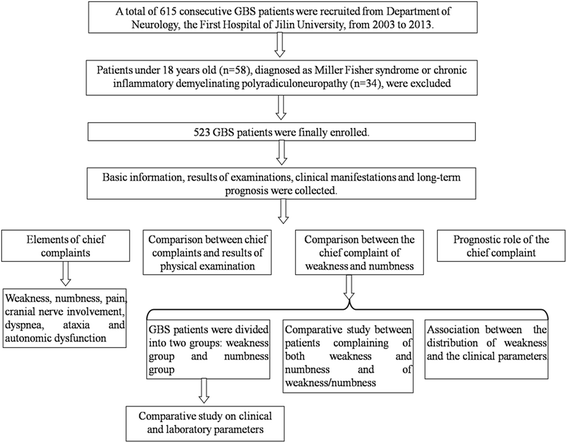



The Usefulness Of Chief Complaints To Predict Severity Ventilator Dependence Treatment Option And Short Term Outcome Of Patients With Guillain Barre Syndrome A Retrospective Study Bmc Neurology Full Text
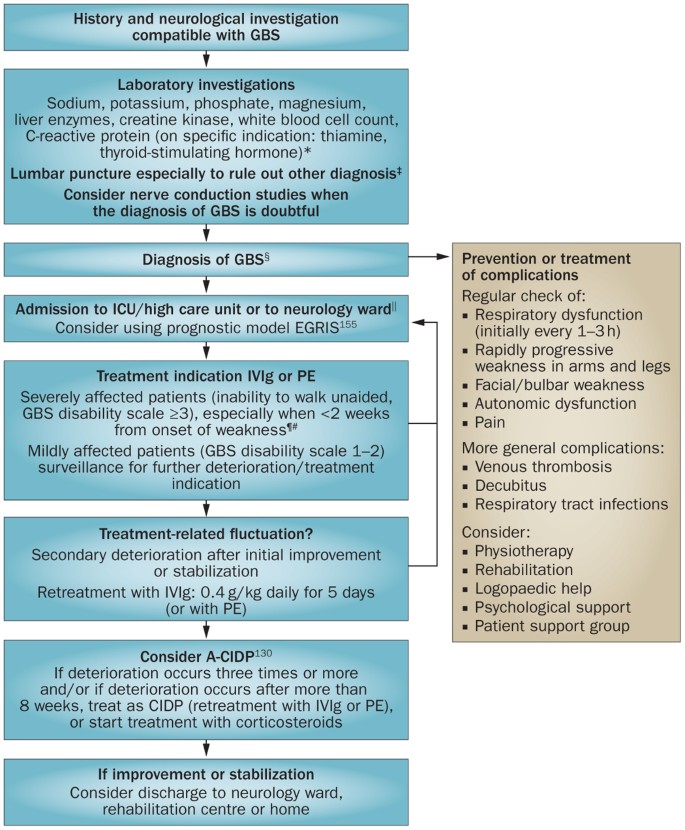



Guillain Barre Syndrome Pathogenesis Diagnosis Treatment And Prognosis Nature Reviews Neurology




Guillain Barre Syndrome American Family Physician




Postoperative Guillain Barre Syndrome A Neurologic Complication That Must Not Be Overlooked A Literature Review Sciencedirect




Residual Neuropathy In Long Term Population Based Follow Up Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Neurology
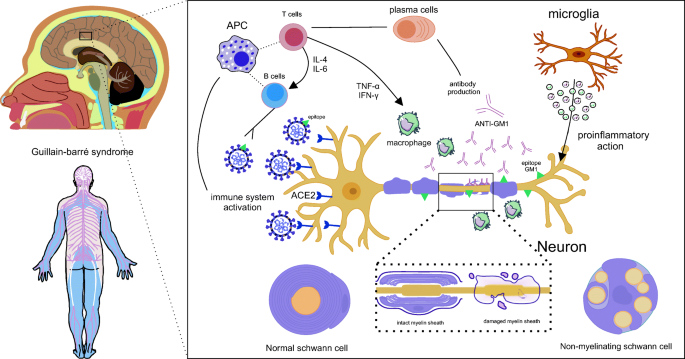



Purinergic Signaling Of Atp In Covid 19 Associated Guillain Barre Syndrome Springerlink




Pdf Guillain Barre Syndrome Semantic Scholar




Guillain Barre Syndrome Mayo Clinic Proceedings




Pdf Guillain Barre Syndrome A Century Of Progress Semantic Scholar




Guillain Barre Syndrome Associated With Sars Cov 2 Infection A Systematic Review And Individual Participant Data Meta Analysis Hasan Journal Of The Peripheral Nervous System Wiley Online Library




Guillain Barre Syndrome Nejm




Pdf Guillain Barre Syndrome Gbs An Orphan Disease




Autoimmunity In Guillain Barre Syndrome Associated With Zika Virus Infection And Beyond Sciencedirect




Scielo Brasil Guillain Barre Syndrome As A Differential Diagnosis Of Low Back Pain Syndrome Guillain Barre Syndrome As A Differential Diagnosis Of Low Back Pain Syndrome




Guillain Barre Syndrome Pdf Medical Specialties Clinical Medicine




Guillain Barre Syndrome The Lancet




Guillain Barre Syndrome And Its Variants As A Manifestation Of Covid 19 A Systematic Review Of Case Reports And Case Series Journal Of The Neurological Sciences



Cureus Neurological Complications Of Covid 19 Guillain Barre Syndrome Following Pfizer Covid 19 Vaccine




The Pathogenesis Of The Demyelinating Form Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Gbs Proteo Peptidomic And Immunological Profiling Of Physiological Fluids Molecular Cellular Proteomics
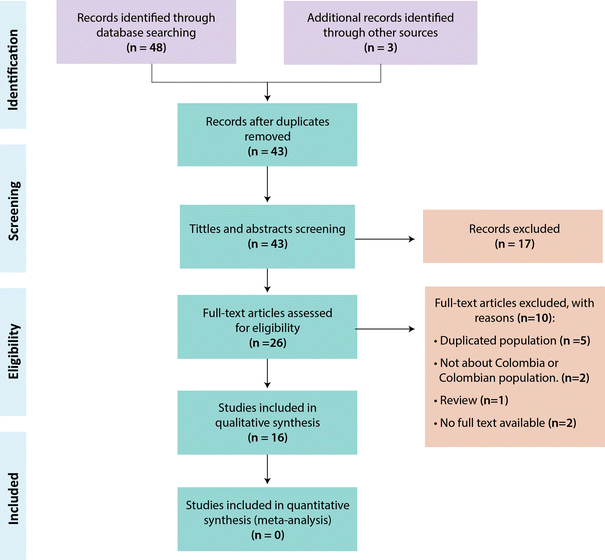



Guillain Barre Syndrome In Colombia Where Do We Stand Now Springerlink




Guillain Barre Syndrome Pathophysiology Pdf




Guillain Barre Syndrome Physiopedia



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿